 Screenshot from the video
Screenshot from the videoIn recent years, advanced model-based and data-driven control methods are unlocking the potential of complex robotics systems, and we can expect this trend to continue at an exponential rate in the near future. However, ensuring safety with these advanced control methods remains a challenge. A well-known tool to make controllers (either Model Predictive Controllers or Reinforcement Learning policies) safe, is the so-called control-invariant set (a.k.a. safe set). Unfortunately, for nonlinear systems, such a set cannot be exactly computed in general. Numerical algorithms exist for computing approximate control-invariant sets, but classic theoretic control methods break down if the set is not exact.
In this presentation I will discuss our recent efforts to address this issue. First, we have designed a novel algorithm for computing a numerical approximation of the largest control invariant set for a robot manipulator. This method is more efficient than other state-of-the-art approaches because it exploits some properties of the dynamics of fully-actuated multi-body systems.
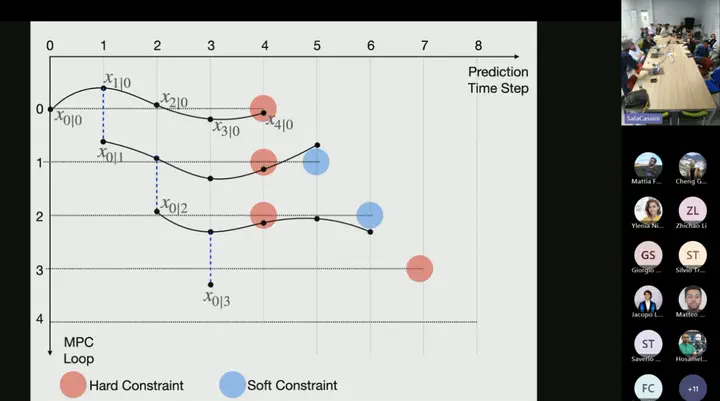
Second, I will present a novel Model Predictive Control scheme that can guarantee recursive feasibility and/or safety under weaker assumptions than classic methods. In particular, recursive feasibility is guaranteed by making the safe-set constraint move backward over the horizon, and assuming that such set satisfies a condition that is weaker than control invariance. Safety is instead guaranteed under an even weaker assumption on the safe set, triggering a safe task-abortion strategy whenever a risk of constraint violation is detected. We evaluated our approach on a simulated robot manipulator, empirically demonstrating that it leads to less constraint violations than state-of-the-art approaches, while retaining good performance in terms of tracking cost, number of completed tasks, and computation times.